Projects
Knowledge-Based Planning (KBP)
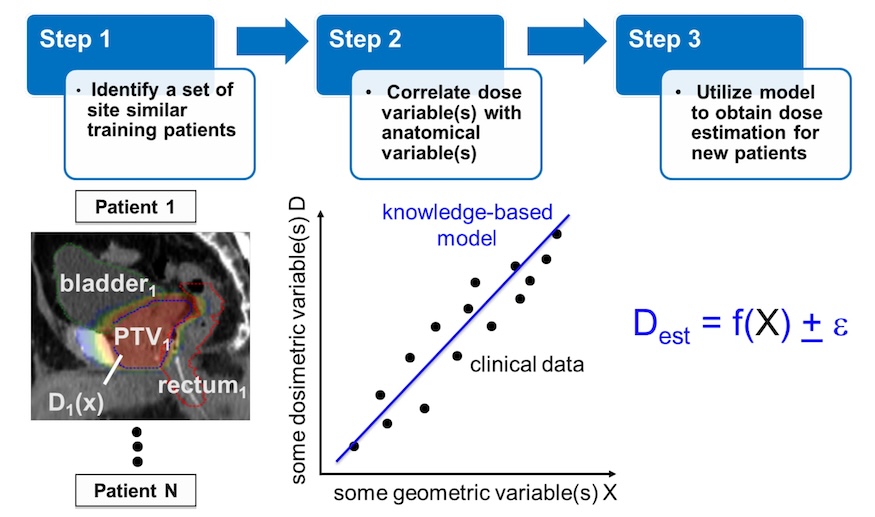
The goal of this ongoing project is bring the maximum amount of information to bear when designing patients' radiotherapy treatments. While every patient presents a unique anatomical challenge in designing an optimal radiotherapy treatment, we can quantitatively utilize prior patient treatments to predict the best achievable radiotherapy plans for new patients. This effort comprises several avenues of investigation, including new algorithms for dose estimation, expanding clinical utilization, providing real-time plan quality feedback for clinicians worldwide, and developing new tools for automated treatment planning.
Moore Lab Personnel Working on KBP Efforts

Kate Cortes
Programmer

Brent Covele, Ph.D.
Post-doctoral fellow

Robert Kaderka, Ph.D.
Medical physics resident

Karoline Kallis, Ph.D.
Post-doctoral fellow

Kelly Kisling, Ph.D.
Faculty physicist
Online Real-time Benchmarking Informatics Technology for RadioTherapy (ORBIT-RT)
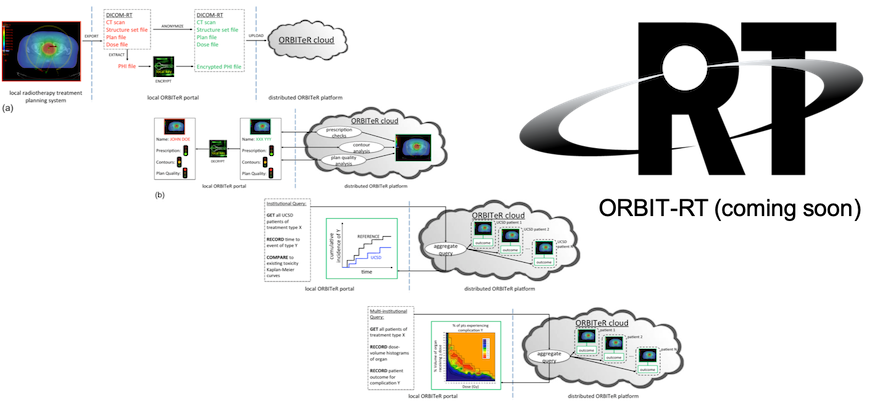
Through a federally-funded effort (sponsored by Agency for Healthcare Research and Qualty) we will soon be launching ORBIT-RT (On-line Real-time Benchmarking Informatics Technology for RadioTherapy), a freely available, on-line knowledge-based radiotherapy plan quality control system. ORBIT-RT will allow clinicians to obtain automatic and immediate feedback on the quality of any individual treatment plan. Using a HIPAA-compliant web-based platform designed to give users real-time radiotherapy plan quality feedback, clinicians all around the world will be able to benchmark their treatment plans against a validated patient-specific plan quality standard as never before.
Moore Lab Personnel Working on ORBIT-RT

Jorge Avila
Programmer

Brent Covele, Ph.D.
Post-doctoral fellow

James Murphy, M.D.
Faculty radiation oncologist

Kartikeya Puri
Programmer
Clinical Implementation of Automated Planning
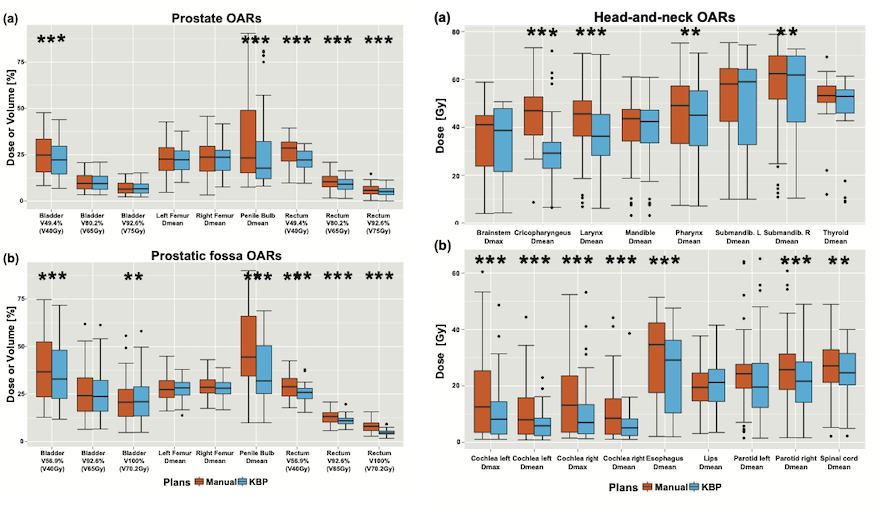
The widespread implementation of automated planning is a core focus of our group's efforts. Broadly speaking, we seek to answer the most critical questions facing automated radiotherapy planning. (1) What effect will automated planning have on aggregated plan quality? (2) How competitive is automated planning compared to human-driven processes? (3) What is the effect on workflow efficiency? (4) How do we maintain and evolve the automated planning routines?
Moore Lab Personnel Working on Clinical Implementation of Automated Planning

Robert Kaderka, Ph.D.
Medical physics resident

Xenia Ray, Ph.D.
Faculty physicist
KBP for Brachytherapy
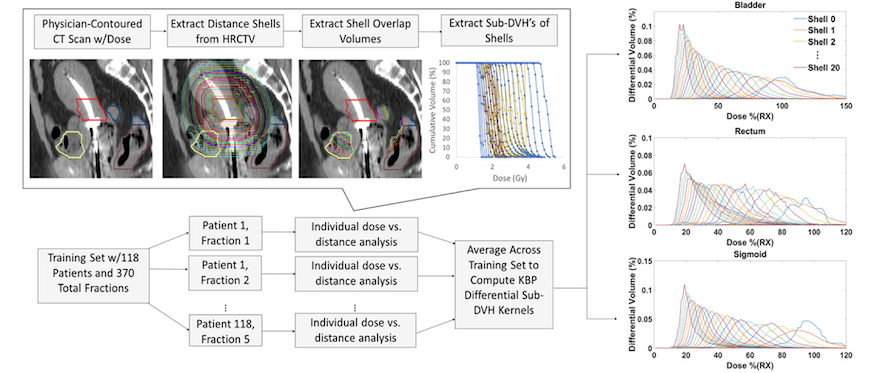
Because its delivery method is so distinct from external beam radiotherapy, brachytherapy presents a unique challenge for patient-specific dose estimation. This effort is dedicated to generating accurate knowledge-based dosimetric predictions in the service of distributed treatment plan quality control for GYN brachytherapy. We are also actively exploring automated planning techniques based on knowledge-based dose predictions, as well as three-dimensional dose estimation for both standard applicators and non-standard needle-based treatments.
Moore Lab Personnel Working on KBP for Brachytherapy

Kate Cortes
Programmer

Karoline Kallis, Ph.D.
Post-doctoral fellow

Jyoti Mayadev, M.D.
Faculty radiation oncologist

Sandra Meyers, Ph.D.
Faculty physicist
New Treatment Design Workflows and Adaptive RT
These efforts are dedicated toward redesigning clinical processes around the automated systems that continue to push the envelope of radiotherapy quality and efficiency. New treatment design workflows that eliminate wasteful processes and compress timeframes could reduce simulation-to-start times, enable sim-less treatments, and facilitate online adaptive radiotherapy.
Collaborators Working on New Treatment Design Workflows
















